Making Nut Butter
Find innovative production technology for making nut butter and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Toast spread, oatmeal topping or salad dressing - nut butter can be used in various ways. Although in a culinary sense classified as such, peanuts, almonds, cashews and pecans, the popular choices for nut butter are, botanically speaking, not nuts. They are processed in a series of nut butter processing equipment to get the creamy, rich product ready for consumption.
Select your nut butter process
Tell us about your production challenge
From nut to butter – steps, ingredients and processing equipment
Nuts make up to 90% of nut butter, accompanied by salt, vegetable oil, dextrose and corn syrup to improve taste and texture. Nut butter production starts with harvest, which is helped by portable mechanical pickers. Harvested nuts undergo a process called shelling, passing through a series of rollers to crack them, followed by screens, blowers, magnets, and destoners to remove the shells.
Once they reach the factory, nuts are dry-roasted. Nuts are then quickly passed to the next piece of nut butter processing equipment – coolers, where they are cooled down to 30°C. Passing the cooled nuts through a gravity separator removes foreign materials before blanching them, in case the chosen nuts have skin. In contrast, the remains are removed by passing them further through the blancher in a continuous stream. Finally, the nuts are processed in a grinder, from where it goes to a stainless steel hopper, which is both a mixing and storage point.

Same but different - Nut Butter vs. Nut Paste
Although almost identical, the ingredients are the characteristic difference between nut butter and nut pastes. While, naturally, nuts are the predominant component of nut butter, other ingredients are added that help to develop taste, smoothness and consistency, such as sugar, emulsifiers and oils. On the other hand, nut pastes are purely nut products without any additions to modify their characteristics. Therefore, it is suitable as an ingredient in products such as ice creams, cookies or chocolates. However, it is essential to highlight that no actual regulations define the difference between a nut butter and a nut paste.
All the butters to go nuts for
Smooth or crunchy, sweetened or natural, added to savory or sweet meals, nut butter and nut pastes offer a wide range of products. The most popular choices are peanut, almond, cashew, walnut and pecan butter or pastes. Some of these products are rich in fiber, protein, and fatty acids as well as vitamins and minerals, which makes them an ideal addition to any meal.

Going nuts for peanut butter
Peanut butter was invented in 1890 by an American doctor as a protein substitute for patients unable to chew meat. It is made by grinding roasted peanuts with added ingredients to enhance its characteristics. One of the key steps in peanut butter processing is blanching – removing the skin. There are two different methods. A heat blanching process exposes peanuts to high temperatures which cause the skin to crack. The second method, water blanching, removes the skin by quickly soaking peanuts in a scalding water bath. The bleaching step is widely used, as blanched peanuts result in a smoother texture, but it is not necessary. Namely, the skin contains extra nutrients and a rich, nutty flavor.

Going nuts for almond, cashew and hazelnut butter
Although peanut butter is the most popular choice, other types of nut butter and pastes have been on the rise. Almond butter might be the second most popular choice as the consistency and production process are almost identical to peanut butter. Cashew butter also follows the production steps closely, but it skips the blanching step as it does not have skin. In contrast to the purely healthy options, hazelnut butter can be mixed with cocoa to make chocolate spreads. However, pure hazelnut butter is rich in Vitamins E and B.
The environmental impact of nut butter production

Although especially popular among the plant-based population, nut butter production yields some adverse environmental impacts. For instance, almonds, known as the least sustainable nut, require large amounts of water. It takes 819 gallons of water to grow one pound of shelled almonds. However, almond farmers have managed to cut down water use by 33% in the past two decades with the help of research-based farming improvements and water-saving technologies. Peanuts, on the other hand, are more sustainable nuts, as they grow in rainy areas requiring less water, similar to pistachio. Like others, the nut butter industry is moving towards more sustainable production methods by improving crop and yield, along with reducing waste.
Processing steps involved in nut butter making
Which nut butter technology do you need?

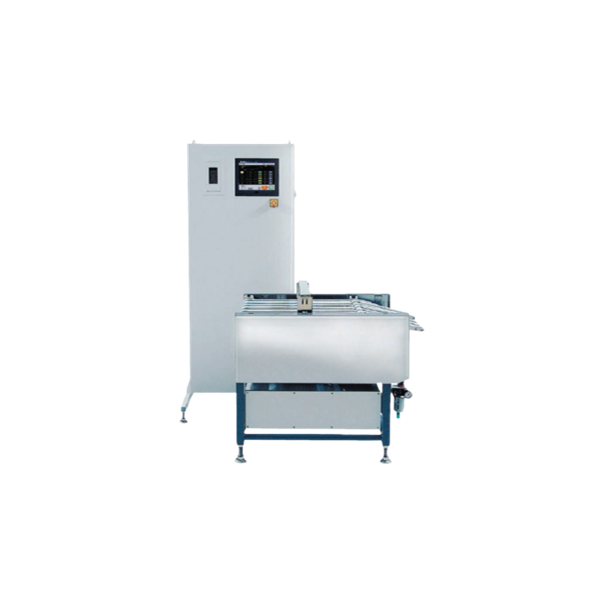
Packaging conveyor for efficient bag handling
In high-volume packaging environments like food processing facilities, manag...

Granulator for nut processing
When handling nuts for various processing applications, achieving consistent granule size can ...
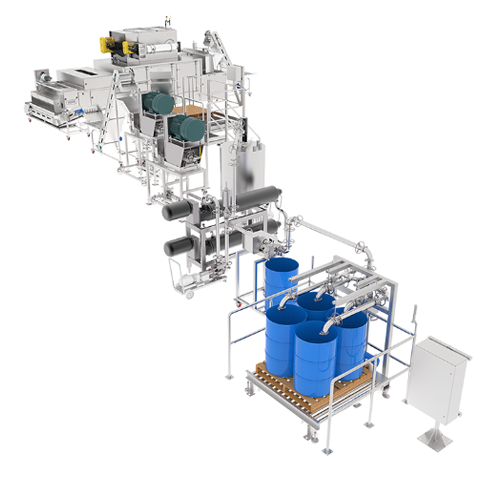
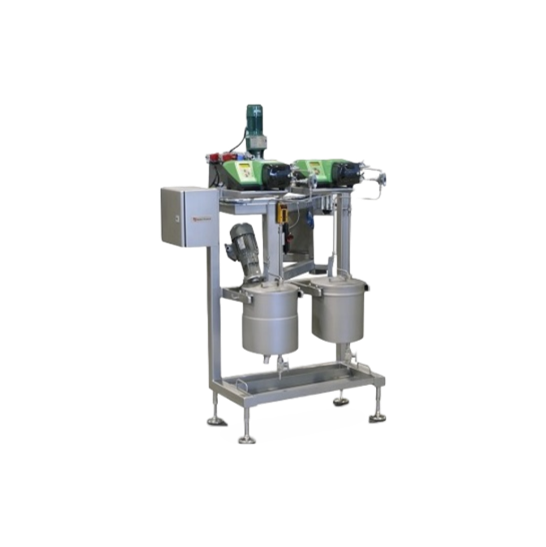
Integrated nut butter production line
Creating high-quality nut butter requires a precise and efficient processing line. Fr...

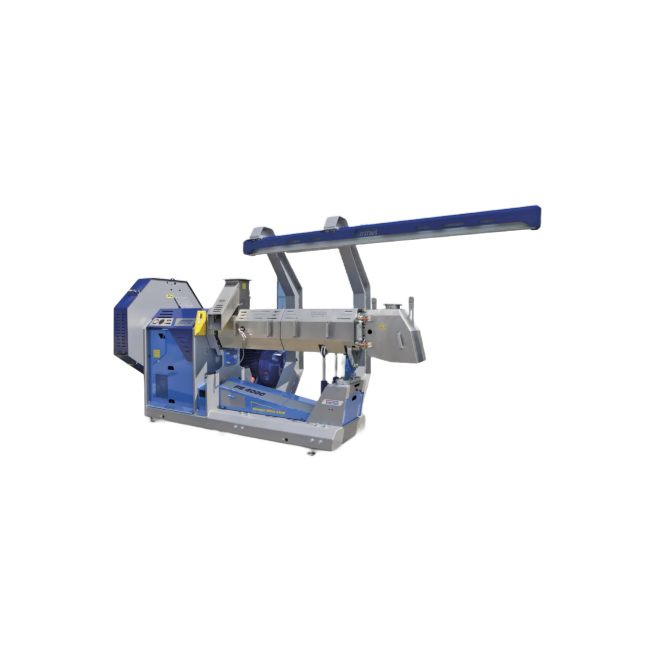
Nut butter mill for snack food processing
In the food processing industry, creating smooth, spreadable nut butter often pr...
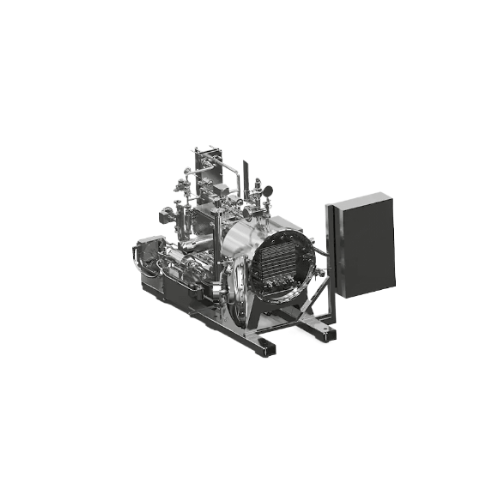
Efficient agitation system for retort packages
In food processing, especially when dealing with retortable rigid or flexib...
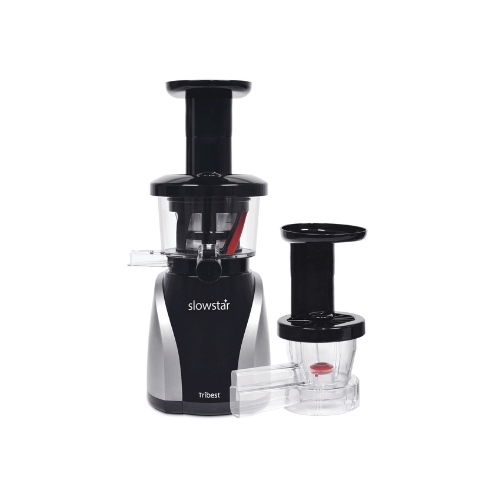

Vertical slow juicer for producing cold pressed juice
In situations where juice extraction quality and nutrient retention...

Cold press juicer for tough vegetables
When juicing tough vegetables like celery, root vegetables, and ginger, traditional ...

Jumbo twin gear slow masticating juicer for high-yield juice extraction
Extracting juice from tough leafy greens, fibro...
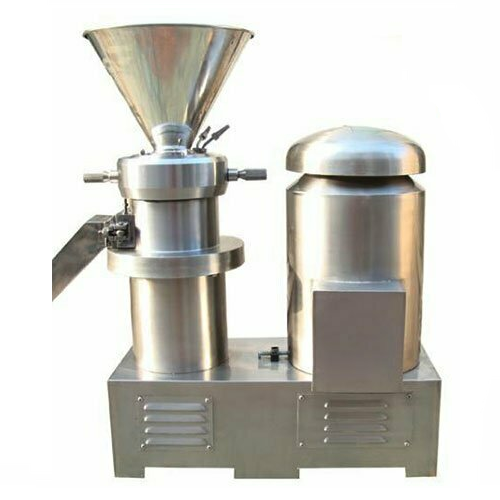

Stainless steel peanut butter grinder
In commercial food production, achieving the right texture and smoothness in nut butt...
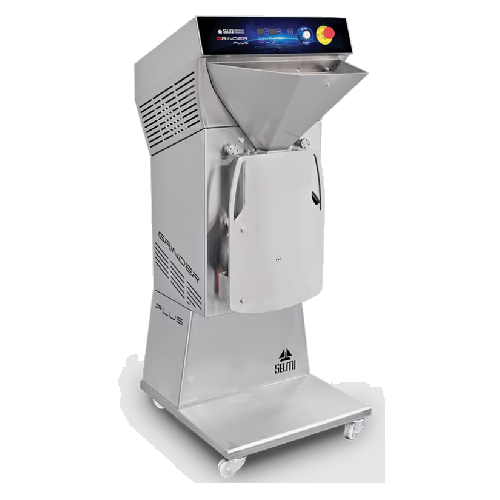

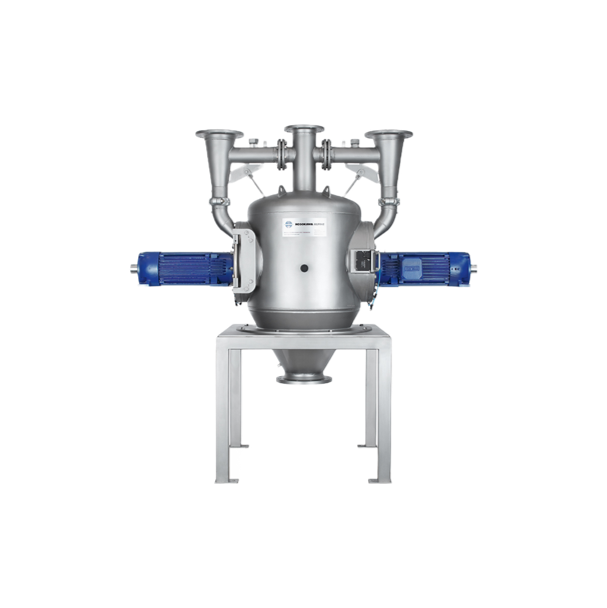
Nuts paste refining mill
In the production of high-quality nut pastes, precise refinement of dried nuts into a consistent, sm...
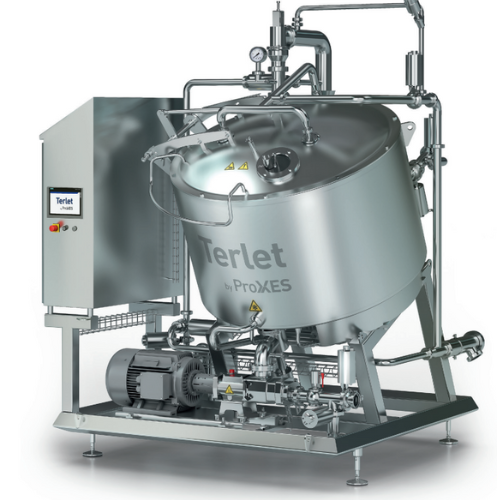

Energy-saving cooling system for vegan products
High-viscosity products like hummus or chunky pasta sauces must be cooled ...

Pilot plant homogeniser
From food to pharma, homogenization is an essential step in the production process that provides unif...
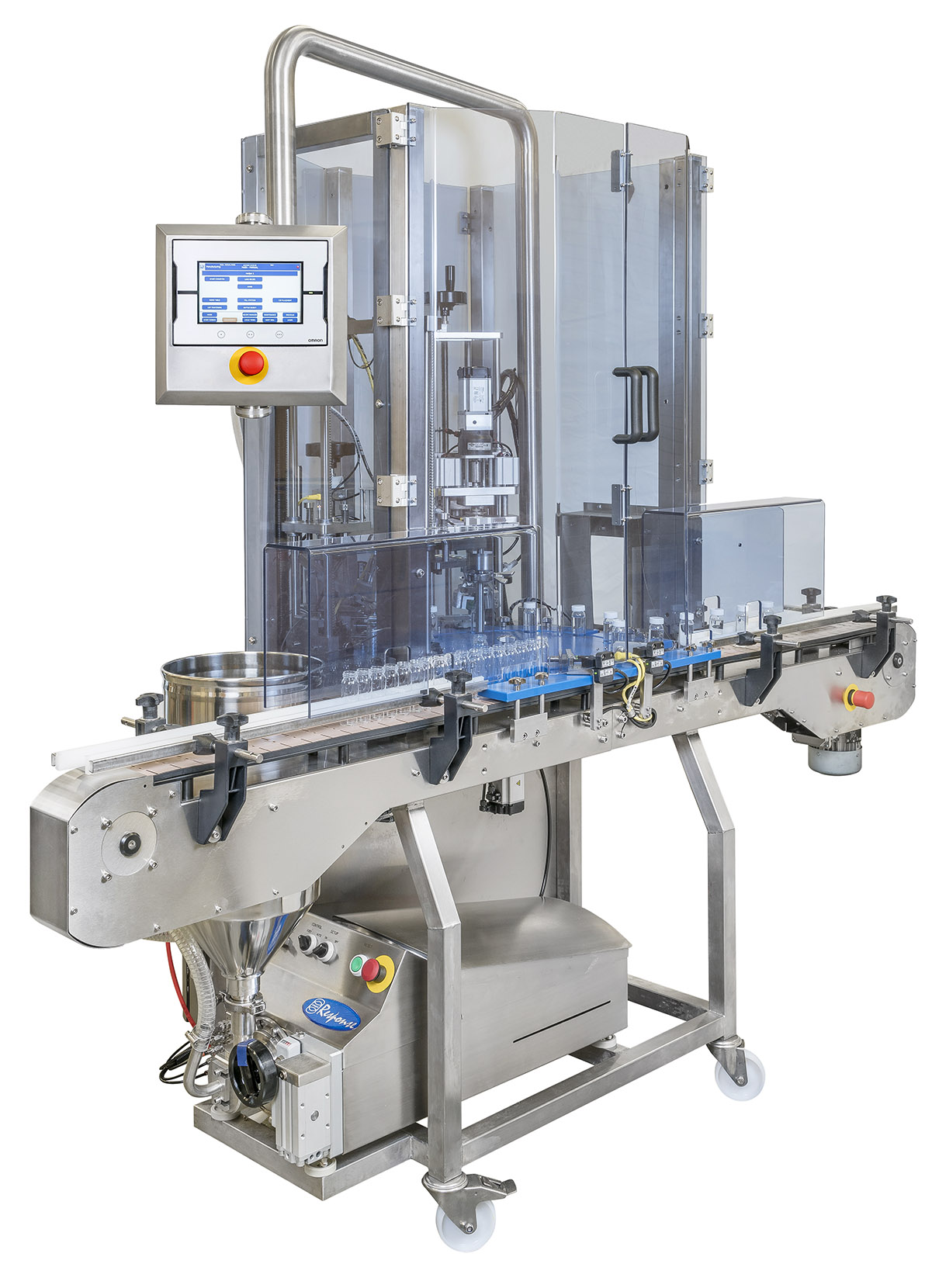

Monobloc filler and capper
If you have separate filling and capping stations you may experience lower throughput rates due t...

Linear automatic bottling machine for liquids
Autonomous filling systems are a very widely utilized solution for the consi...

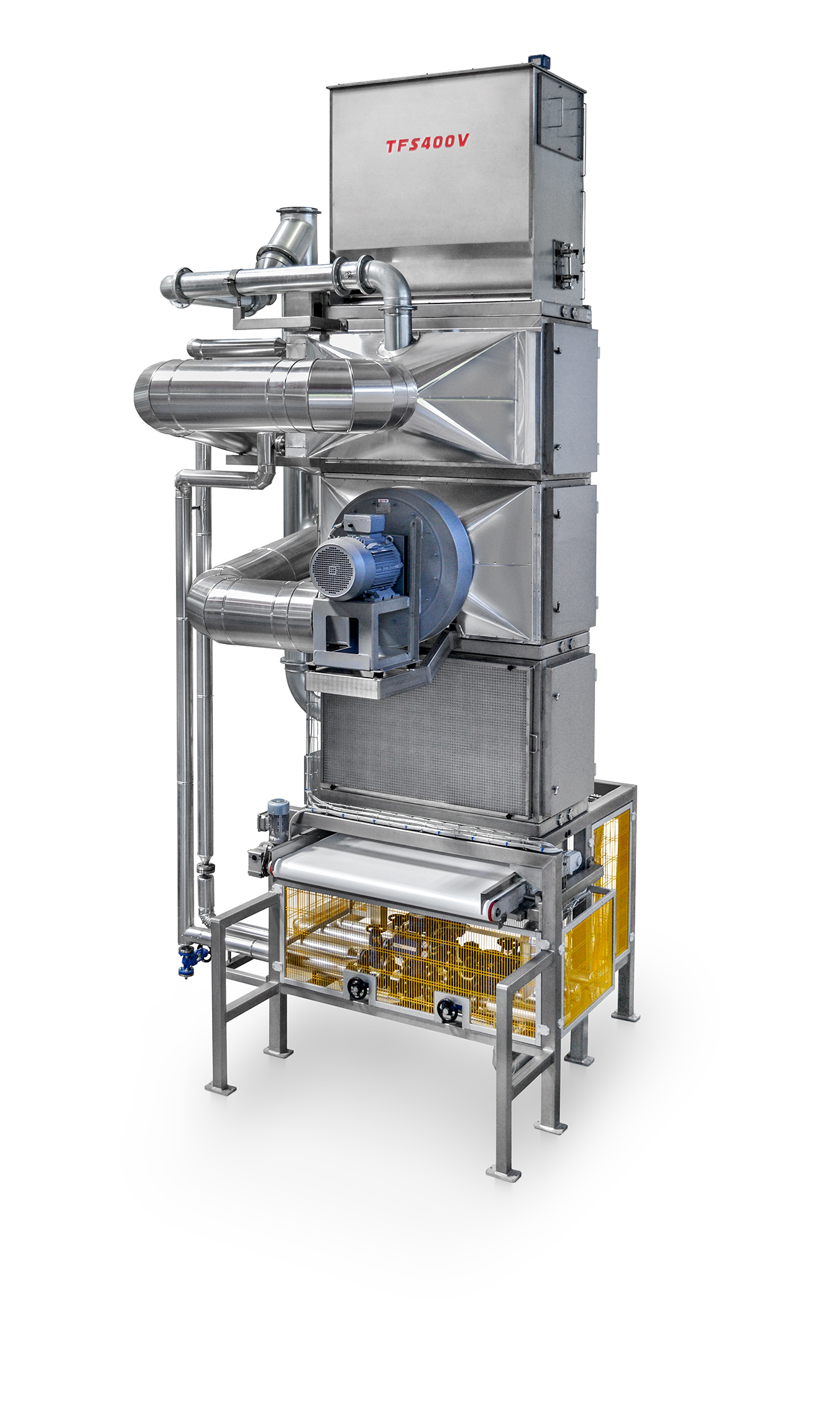
Industrial melter for chocolate rework
Wastage or out-of-specification products are not uncommon in the chocolate manufactu...

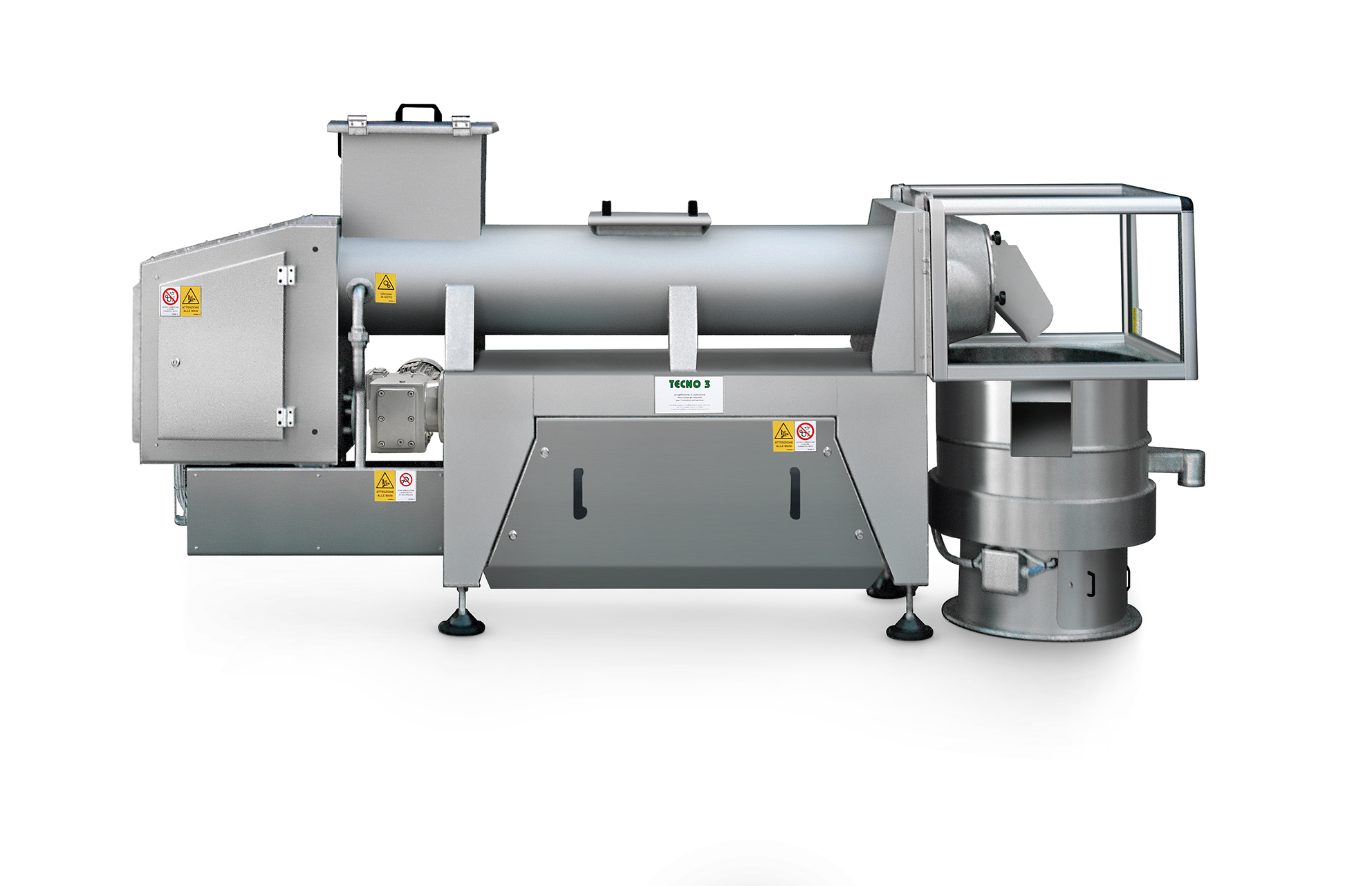
Industrial Nut Roaster
Moisture considerably depletes the shelf life of nut products. At the same time, however, manufacturer...
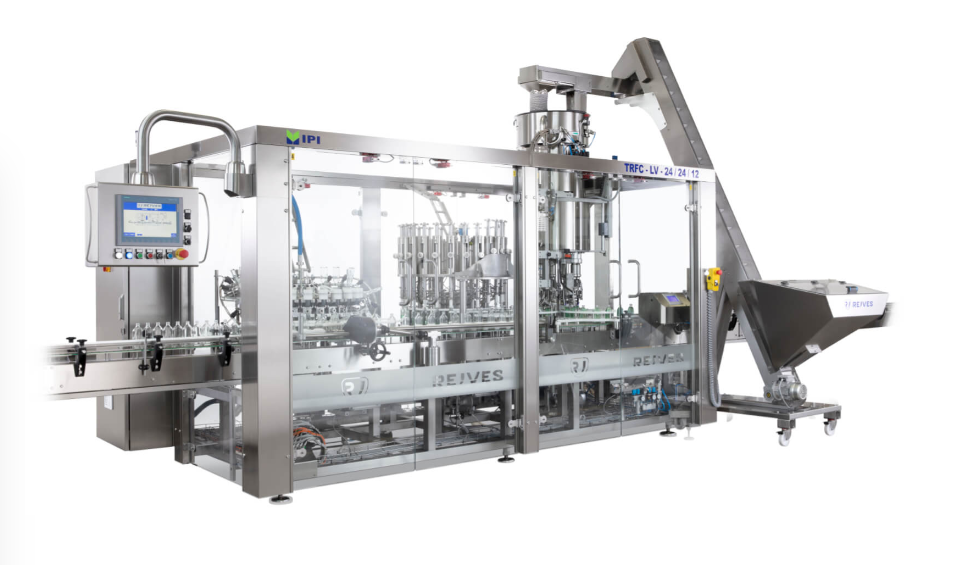

Bottle filling and capping monobloc
Spillage and overfilling are common problems in most production lines for bottled produ...

Multifunction case packer for bottles and jars
New ways of packaging products are popping up all the time on the market. T...
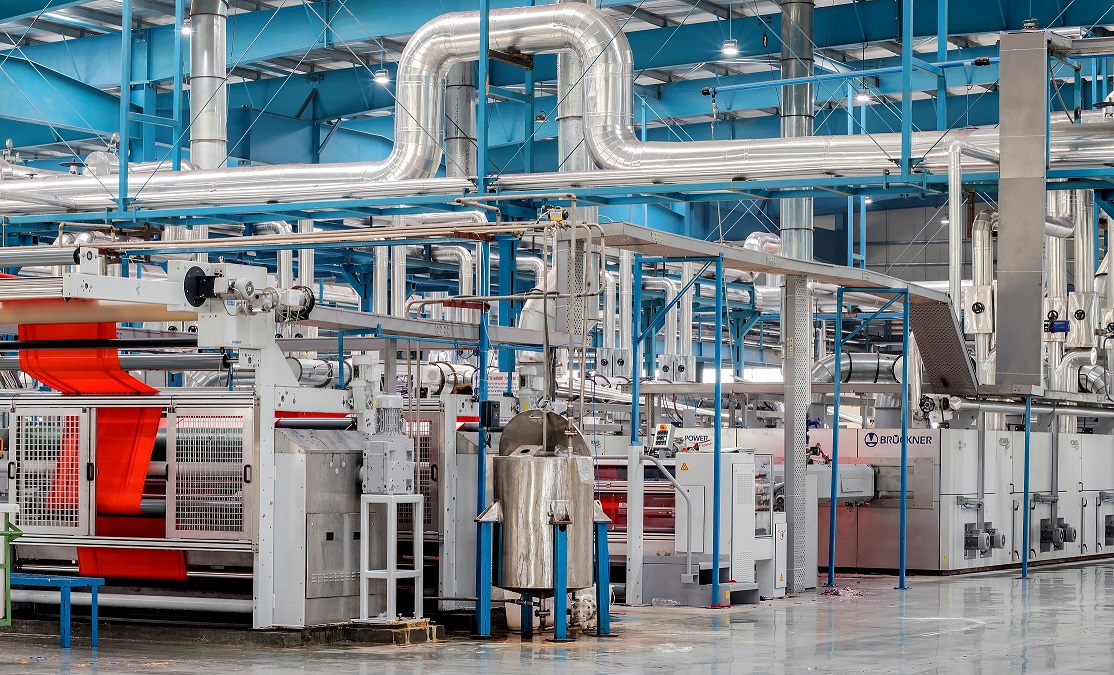

Industrial fine milling equipment for nuts
In a bakery environment fruit jams are often used for the decoration or filling...

Standard FFS machine for spreads and sauces in mini portions
In the food industry, from a microbiological point of view,...

Automatic bottling machine for beverage
One of the biggest challenges when bottling beverage drinks is that many of the bot...
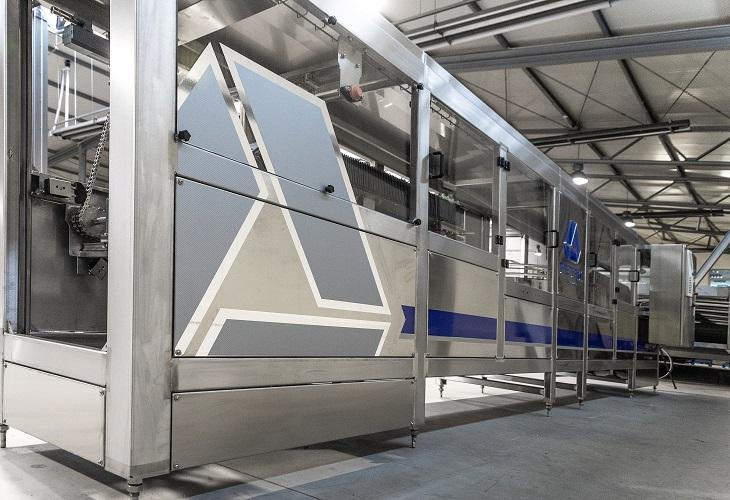

Industrial bottle sterilizer
Sterilization is an important process in the beverage industry to kill microorganisms. It is im...

High pressure electric laboratory homogenizer
It’s vital that small units for experimentation can scale up with 100% accur...
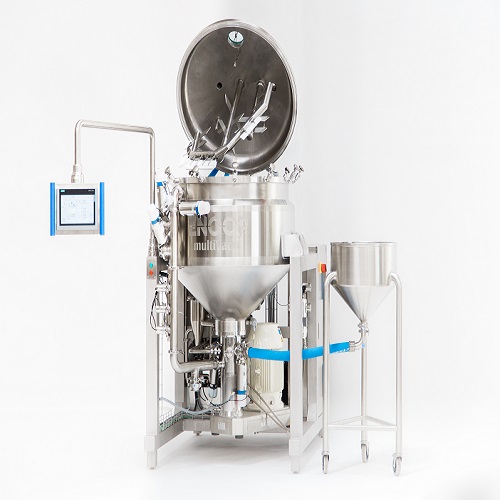

Vacuum based homogenizer
When producing liquid and viscous products such as mayonnaise, sauces, dressings and ketchup it’s vi...

Filling machine for viscous products
Chocolate paste and other viscous liquids require special handling to obtain the optim...
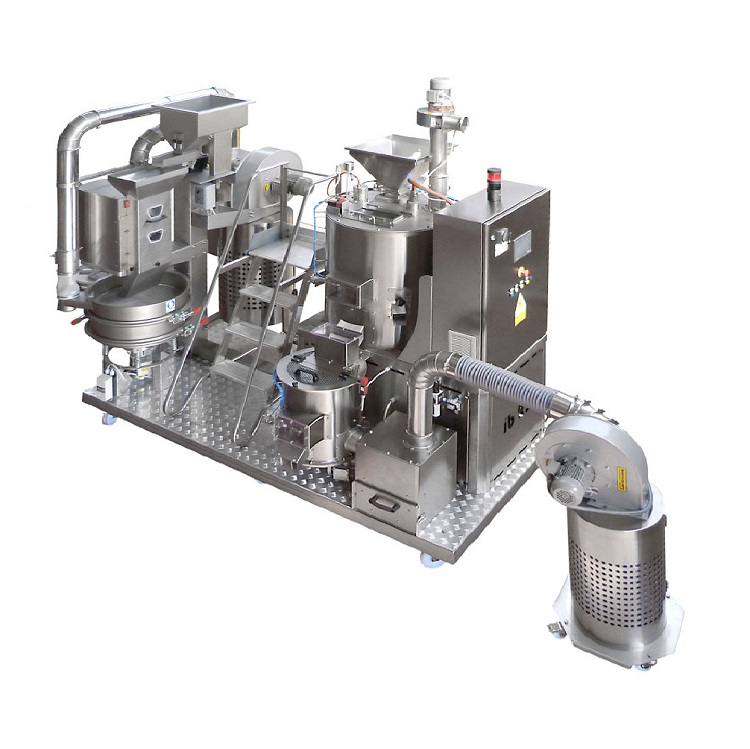
R&D roaster for cocoa beans
When designing a new chocolate line or experimenting with new ingredients for existing processes...
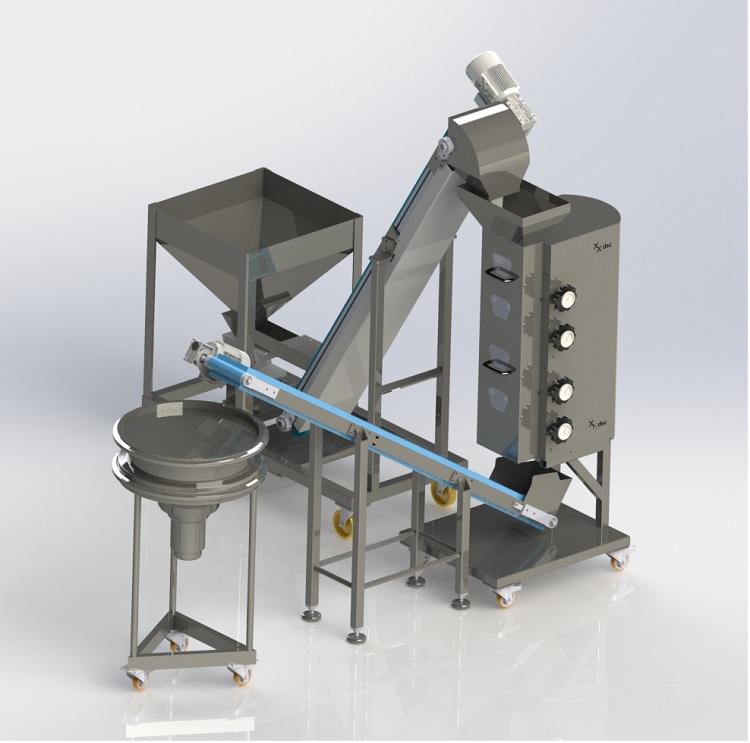

Small scale linear sieve for nuts
Removing dust and grading grains is an important part of producing a high quality chopped...
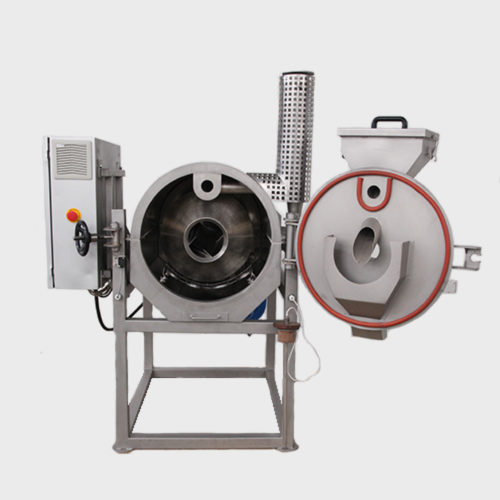

Compact cylindrical roaster for beans, nibs and nuts
Roasting times and temperature can vary depending on the type of pro...
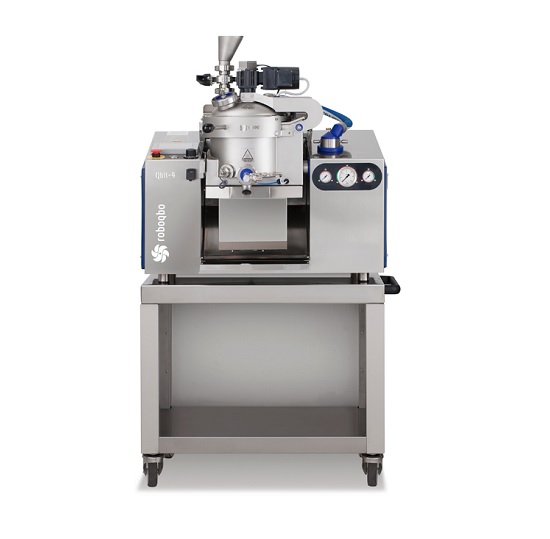

Easy to use food processor for gastronomy sauces and pastes
For the development and production of high quality gastronom...
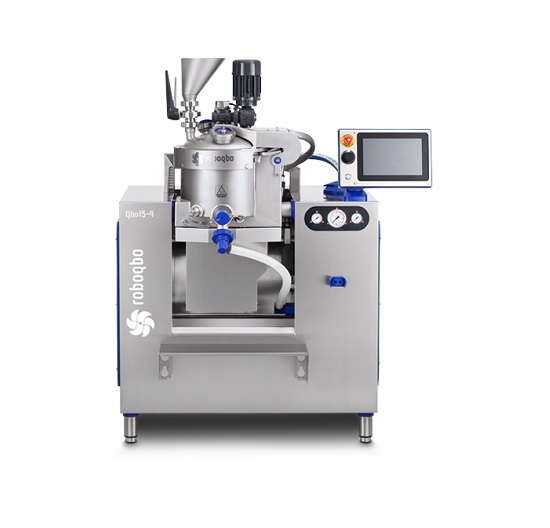

Multi-functional food processor for a high sugar percentage pastes production
For the development and production of hi...
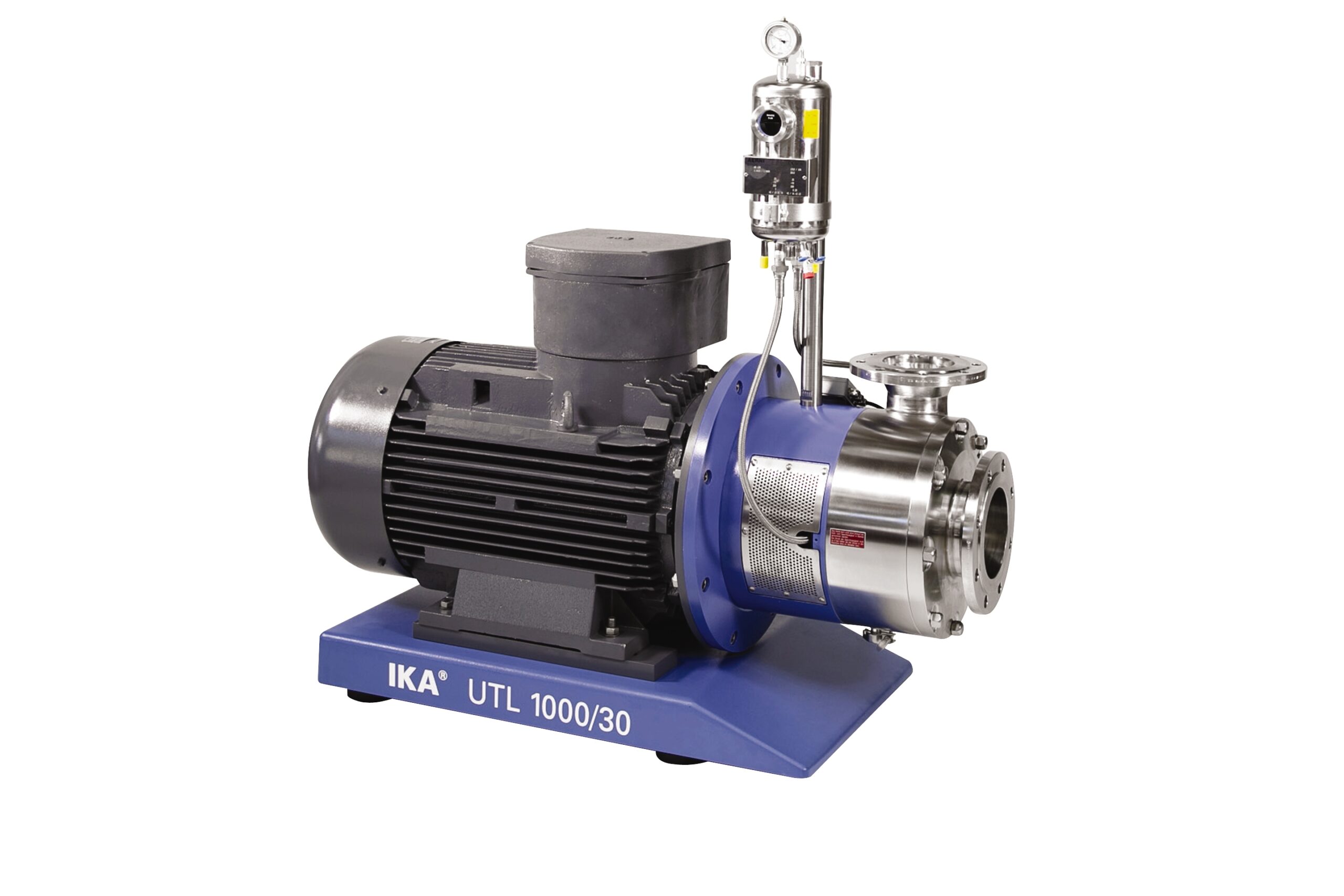

Economic dispersing machine for emulsions and suspensions
For products of medium viscosity and relatively consistent par...
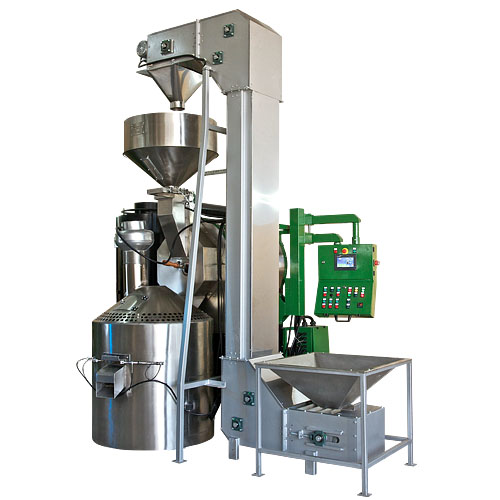

Nut roaster
Nut roaster that guarantees a high-quality roasting of nuts and seeds with a batching capacity of 40 and 120 kg, d...
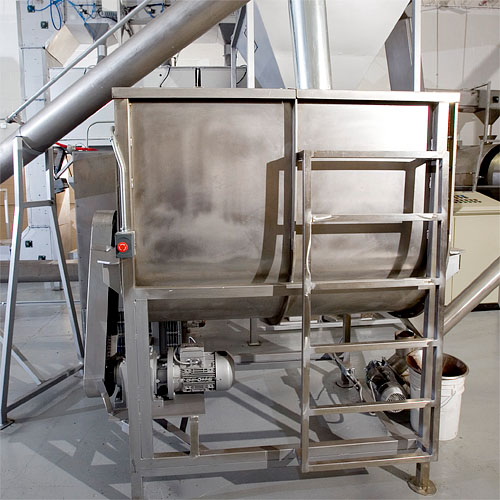

Basic mixer for granular foods
Straightforward blending solution for mixtures of beans, nuts, berries & powdered foods, ...
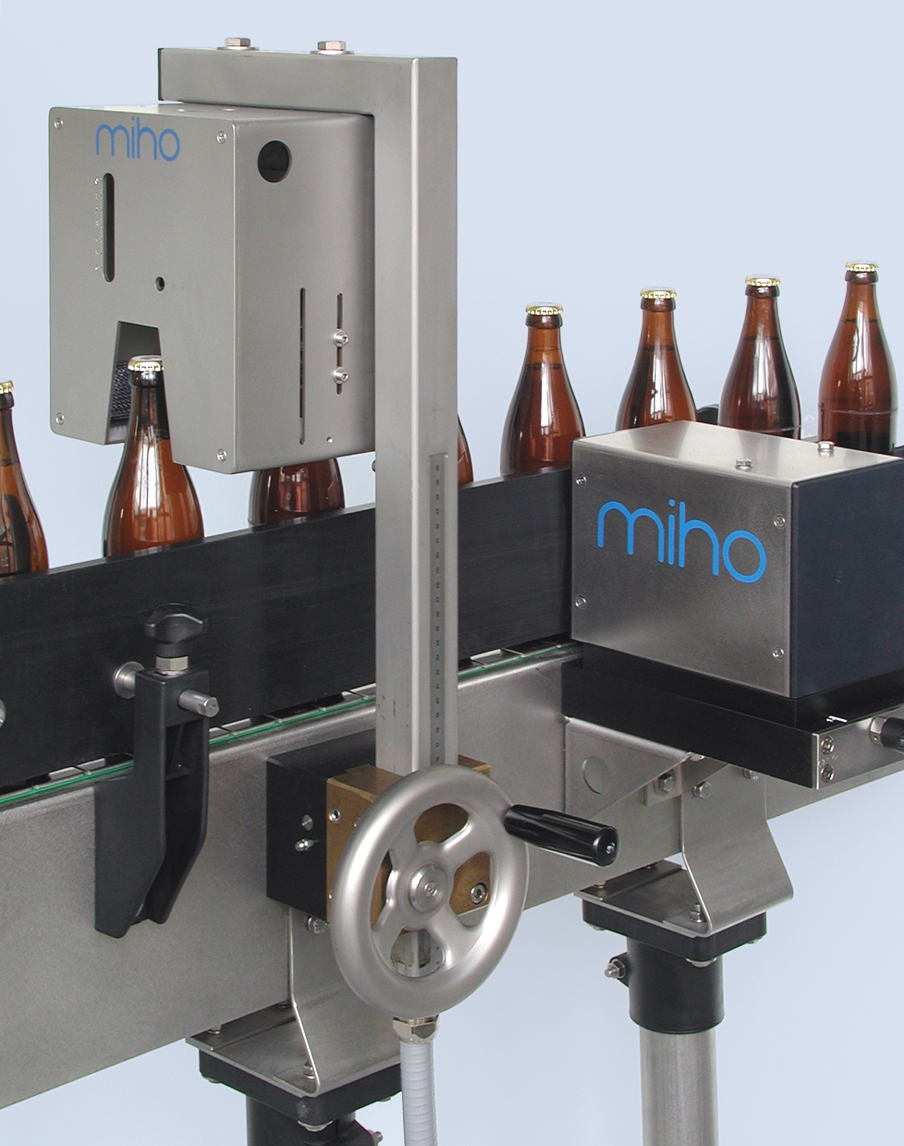

High-frequency fill level controller
In terms of high-frequency technology, the fill level detection is considered a standa...

Infrared rotating drum steriliser
Sterilisation of foodstuffs is vital to maintain uncompromising standards of hygiene and ...
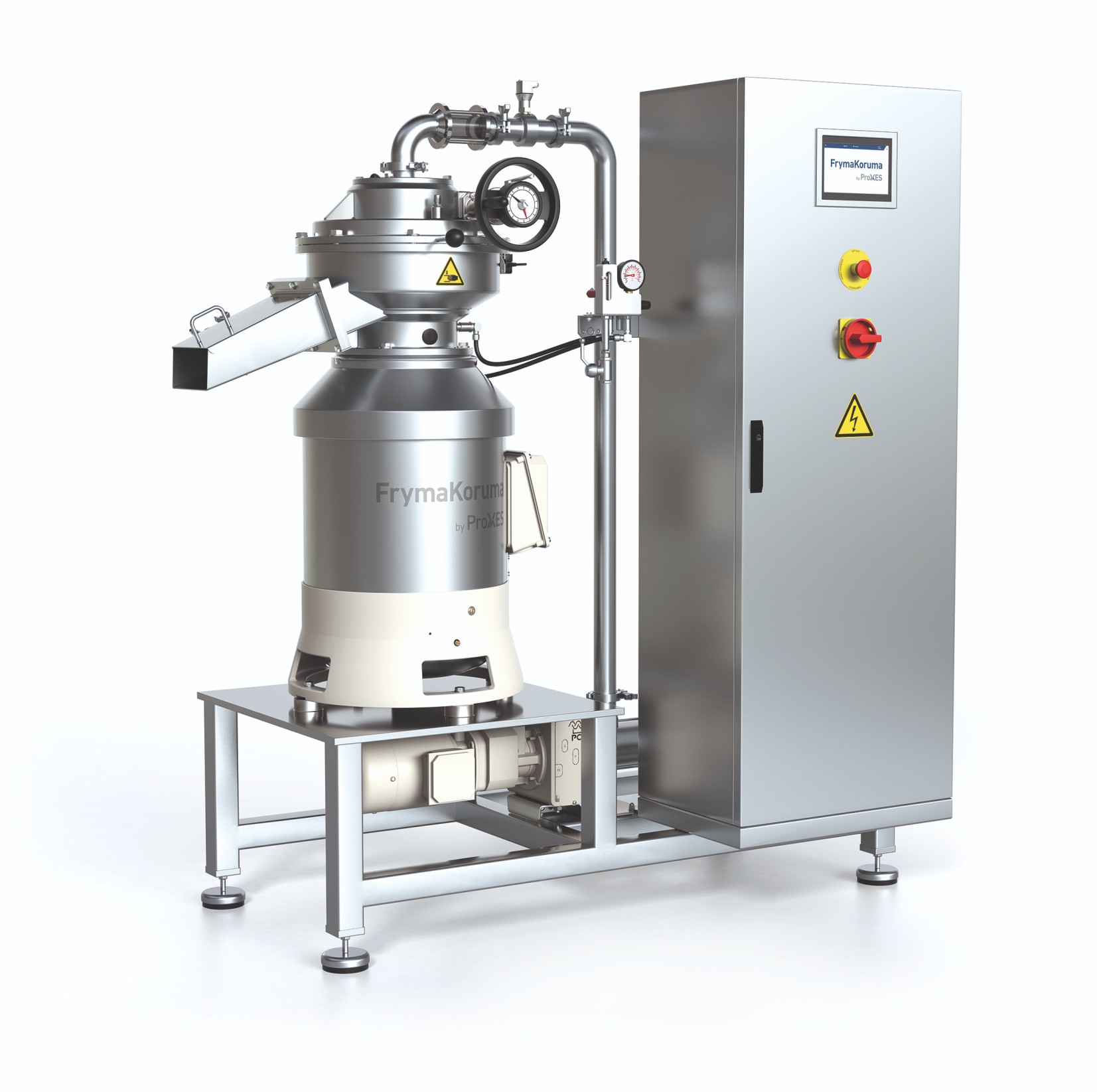

Versatile stone mill machine
In the food industry, when it comes to milling a wide range of products such as seeds and nuts ...